Further Mathematics/Mathematics (Elective) Objective Tests
Welcome to Our Site
I greet you this day,
These are the solutions to the Further Mathematics (Elective Mathematics) multiple-choice questions on the
Objective Tests.
The TI-84 Plus CE shall be used for applicable questions.
Formulas, rules/laws, and theorems are not stated here. However, they are stated on the website for each topic
as applicable. Please review them there.
The link to the video solutions will be provided for you. Please subscribe to the YouTube channel to be notified
of upcoming livestreams.
You are welcome to ask questions during the video livestreams.
If you find these resources valuable and if any of these resources were helpful in your passing the
Further
Mathematics tests/exams, please consider making a donation:
Cash App: $ExamsSuccess or
cash.app/ExamsSuccess
PayPal: @ExamsSuccess or
PayPal.me/ExamsSuccess
Google charges me for the hosting of this website and my other
educational websites. It does not host any of the websites for free.
Besides, I spend a lot of time to type the questions and the solutions well.
As you probably know, I provide clear explanations on the solutions.
Your donation is appreciated.
Comments, ideas, areas of improvement, questions, and constructive
criticisms are welcome.
Feel free to contact me. Please be positive in your message.
I wish you the best.
Thank you.
Find the value of $(-3 * 7) + 5$
$ A.\;\; 27 \\[3ex] B.\;\; 15 \\[3ex] C.\;\; -15 \\[3ex] D.\;\; -27 \\[3ex] $
$ p * q = (p + q)^2 + 2p \\[3ex] (-3 * 7) + 5 \\[3ex] = (-3 + 7)^2 + 2(-3) + 5 \\[3ex] = 4^2 - 6 + 5 \\[3ex] = 16 - 6 + 5 \\[3ex] = 15 $
Find the value of x.
$ A.\;\; 6 \\[3ex] B.\;\; 3 \\[3ex] C.\;\; 2 \\[3ex] D.\;\; 1 \\[3ex] $
$ (3x - 1), (x + 1), (x - 1) \\[3ex] \text{common ratio, } r = \dfrac{x + 1}{3x - 1} = \dfrac{x - 1}{x + 1} \\[5ex] (3x - 1)(x - 1) = (x + 1)(x + 1) \\[3ex] 3x^2 - 3x - x + 1 = x^2 + x + x + 1 \\[3ex] 3x^2 - 4x + 1 = x^2 + 2x + 1 \\[3ex] 3x^2 - x^2 - 4x - 2x + 1 - 1 = 0 \\[3ex] 2x^2 - 6x = 0 \\[3ex] 2x(x - 3) = 0 \\[3ex] 2x = 0 \hspace{1em}OR\hspace{1em} x - 3 = 0 \\[3ex] x = \dfrac{0}{2} \hspace{1em}OR\hspace{1em} x = 3 \\[5ex] x = 0, 3 \\[3ex] But\;\; x \gt 0 \\[3ex] Hence\;\; x = 3 $
$ A.\;\; 1 \hspace{1em}or\hspace{1em} 4 \\[3ex] B.\;\; 1 \hspace{1em}or\hspace{1em} -4 \\[3ex] C.\;\; -1 \hspace{1em}or\hspace{1em} 4 \\[3ex] D.\;\; -1 \hspace{1em}or\hspace{1em} -4 \\[3ex] $
$ \left(3^{x^2}\right) = \dfrac{1}{81}\left(3^{5x}\right) \\[6ex] 3^{x^2} = \dfrac{1}{3^4}\left(3^{5x}\right) \\[7ex] 3^{x^2} = 3^{5x - 4}...Law\;2...Exp \\[5ex] \text{same base; equate exponents} \\[3ex] x^2 = 5x - 4 \\[3ex] x^2 - 5x + 4 = 0 \\[3ex] (x - 1)(x - 4) = 0 \\[3ex] x - 1 = 0 \hspace{3em}OR\hspace{3em} x - 4 = 0 \\[3ex] x = 1 \hspace{3em}OR\hspace{3em} x = 4 \\[3ex] $ Check
| LHS | RHS |
|---|---|
|
$
3^{x^2} \\[4ex]
x = 1 \\[3ex]
3^{1^2} \\[4ex]
3^1
$
$ 3^{x^2} \\[4ex] x = 4 \\[3ex] 3^{4^2} \\[4ex] 3^{16} $ |
$
\dfrac{1}{81}\left(3^{5x}\right) \\[6ex]
x = 1 \\[3ex]
\dfrac{1}{3^4}\left(3^{5(1)}\right)...Law\;5...Exp \\[7ex]
\dfrac{3^5}{3^4} \\[7ex]
3^{5 - 4} ...Law\;2...Exp \\[5ex]
3^1
$
$ \dfrac{1}{81}\left(3^{5x}\right) \\[6ex] x = 4 \\[3ex] \dfrac{1}{3^4}\left(3^{5(4)}\right)...Law\;5...Exp \\[7ex] \dfrac{3^{20}}{3^4} \\[7ex] 3^{20 - 4} ...Law\;2...Exp \\[5ex] 3^{16} $ |


$ A.\;\; x = \dfrac{9}{8} \\[5ex] B.\;\; x = \dfrac{8}{9} \\[5ex] C.\;\; x = -\dfrac{8}{9} \\[5ex] D.\;\; x = -\dfrac{9}{8} \\[5ex] $
The equation of the axis of symmetry of a quadratic function is the x-coordinate of the vertex
$ y = -4x^2 + 9x - 13 \\[3ex] Compare\;\;to: y = ax^2 + bx + c \\[3ex] a = -4 \\[3ex] b = 9 \\[3ex] x-coordinate \;\;of\;\;the\;\;vertex \\[3ex] = -\dfrac{b}{2a} \\[5ex] = -\dfrac{9}{2(-4)} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{9}{8} \\[3ex] $ This is the axis of symmetry of the quadratic function.
$ A.\;\; \dfrac{\log_{10}p \times \log_{10}\sqrt{q}}{\log_{10}r} \\[6ex] B.\;\; \log_{10} p + \dfrac{1}{2}\log_{10}q + \log_{10}r \\[5ex] C.\;\; \dfrac{\log_{10} p + \dfrac{1}{2}\log_{10} q}{\log_{10} r} \\[7ex] D.\;\; \log_{10} p + \dfrac{1}{2}\log_{10} q - \log_{10} r \\[5ex] $
$ \log_{10} x = \log x \\[3ex] x = \dfrac{p\sqrt{q}}{r} \\[3ex] \text{Introduce log to both sides} \\[3ex] \log x = \log\left(\dfrac{p\sqrt{q}}{r}\right) \\[5ex] = \log p + \log \sqrt{q} - \log r ...Laws\;1\;\;and\;\;2...Log \\[4ex] = \log p + \log q^{\dfrac{1}{2}} - \log r ...Law\;7...Exp \\[5ex] = \log p + \dfrac{1}{2}\log q - \log r ...Law\;5...Log \\[5ex] = \log_{10} p + \dfrac{1}{2}\log_{10}q + \log_{10}r $
$ A.\;\; \dfrac{11}{6} \\[5ex] B.\;\; \dfrac{6}{11} \\[5ex] C.\;\; -\dfrac{6}{11} \\[5ex] D.\;\; -\dfrac{11}{6} \\[5ex] $
$ f(x) = \dfrac{5x + 8}{7 - 3x},\;\;x \ne \dfrac{7}{3} \\[5ex] y = \dfrac{5x + 8}{7 - 3x} \\[5ex] \text{Interchange x and y} \\[3ex] x = \dfrac{5y + 8}{7 - 3y} \\[5ex] \text{Solve for y} \\[3ex] 5y + 8 = x(7 - 3y) \\[3ex] 5y + 8 = 7x - 3xy \\[3ex] 5y + 3xy = 7x - 8 \\[3ex] y(5 + 3x) = 7x - 8 \\[3ex] y = \dfrac{7x - 8}{5 + 3x} \\[5ex] \text{This value of y is the inverse function} \\[3ex] y^{-1} = \dfrac{7x - 8}{5 + 3x} \\[5ex] f^(-1)(x) = \dfrac{7x - 8}{3x + 5} \\[5ex] f^(-1)(2) = \dfrac{7(2) - 8}{3(2) + 5} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{14 - 8}{6 + 5} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{6}{11} $
$ A.\;\; \dfrac{1}{6} \\[5ex] B.\;\; \dfrac{2}{3} \\[5ex] C.\;\; 2 \\[3ex] D.\;\; 3 \\[3ex] $
$ \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}} \\[3ex] = \dfrac{1}{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}...Law\;7...Exp \\[7ex] = x^{-\dfrac{1}{2}} ...Law\;6...Exp \\[5ex] \implies \\[3ex] \displaystyle\int \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}} dx \\[5ex] = \displaystyle\int x^{-\dfrac{1}{2}} dx \\[5ex] = \dfrac{x^{-\dfrac{1}{2} + 1}}{-\dfrac{1}{2} + 1}...Power\;\;Rule \\[7ex] = \dfrac{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{\dfrac{1}{2}} \\[7ex] = x^{\dfrac{1}{2}} \div \dfrac{1}{2} \\[5ex] = \sqrt{x} * \dfrac{2}{1} \\[5ex] = 2\sqrt{x} \\[5ex] \implies \\[3ex] \displaystyle\int_4^9 \left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\right) dx \\[7ex] = \left[2\sqrt{x}\right]_4^9 \\[5ex] = 2\sqrt{9} - 2\sqrt{4} \\[3ex] = 2(\sqrt{9} - \sqrt{4}) \\[3ex] = 2(3 - 2) \\[3ex] = 2(1) \\[3ex] = 2 \\[3ex] y = 2 $

$ A.\;\; \dfrac{5}{3} \\[5ex] B.\;\; 3 \\[3ex] C.\;\; 5 \\[3ex] D.\;\; 15 \\[3ex] $
$ 5 + \dfrac{10}{3} + \dfrac{20}{9} + \\[5ex] \text{first term, } a = 5 \\[3ex] \text{common ratio, } r = \dfrac{10}{3} \div 5 \\[5ex] r = \dfrac{10}{3} * \dfrac{1}{5} \\[5ex] r = \dfrac{2}{3} \\[5ex] \text{Sum to infinity, } S_\infty = \dfrac{a}{1 - r} \\[5ex] = a \div (1 - r) \\[3ex] = 5 \div \left(1 - \dfrac{2}{3}\right) \\[5ex] = 5 \div \dfrac{1}{3} \\[5ex] = 5 * 3 \\[3ex] = 15 $
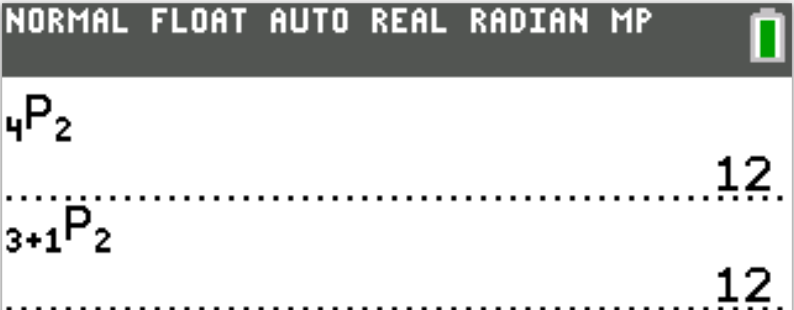
$ A.\;\; 12 \\[3ex] B.\;\; 6 \\[3ex] C.\;\; 4 \\[3ex] D.\;\; 3 \\[3ex] $
$ ^nP_r = \dfrac{n!}{(n - r)!} \\[5ex] ^{(n + 1)}P_2 = 12 \\[5ex] \dfrac{(n + 1)!}{(n + 1 - 2)!} = 12 \\[5ex] \dfrac{(n + 1) \cdot n \cdot (n - 1)!}{(n - 1)!} = 2 \\[5ex] n^2 + n = 12 \\[3ex] n^2 + n - 12 = 0 \\[3ex] (n + 4)(n - 3) = 0 \\[3ex] n + 4 = 0 \hspace{1em}OR\hspace{1em} n - 3 = 0 \\[3ex] n = -4 \hspace{1em}OR\hspace{1em} n = 3 \\[3ex] n \;\; \text{cannot be negative because it has to be countable} \\[3ex] \therefore n = 3 $
$ A.\;\; (x + 2) \\[3ex] B.\;\; (x + 1) \\[3ex] C.\;\; (x - 3) \\[3ex] D.\;\; (x + 3) \\[3ex] $
$ x^3 + 2x^2 - 3x \\[3ex] x(x^2 + 2x - 3) \\[3ex] x(x + 3)(x - 1) \\[3ex] $ Option D. is the correct answer.
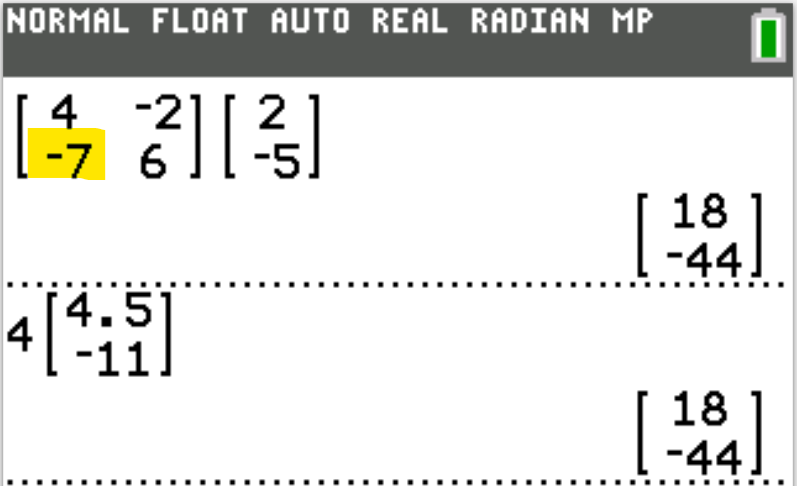
$ A.\;\; -9 \\[3ex] B.\;\; -7 \\[3ex] C.\;\; 7 \\[3ex] D.\;\; 9 \\[3ex] $
$ \begin{bmatrix} 4 & -2 \\[2ex] x & 6 \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} 2 \\[2ex] -5 \end{bmatrix} = 4\begin{bmatrix} 4.5 \\[2ex] -11 \end{bmatrix} $
$ \begin{bmatrix} 4(2) + (-2)(-5) \\[2ex] x(2) + 6(-5) \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 4(4.5) \\[2ex] 4(-11) \end{bmatrix} $
$ \begin{bmatrix} 8 + 10 \\[2ex] 2x - 30 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 18 \\[2ex] -44 \end{bmatrix} $
$ 2x - 30 = -44 \\[3ex] 2x = -44 + 30 \\[3ex] 2x = -14 \\[3ex] x = -\dfrac{14}{2} \\[5ex] x = -7 $
$ A.\;\; -5 \\[3ex] B.\;\; -4 \\[3ex] C.\;\; -3 \\[3ex] D.\;\; -2 \\[3ex] $
The curve $y = 3x^2 + 10x + 2$ passes through (x, −6)
We do not know the value of x (we need to find it)
But we do know the value of y = −6
$ y = 3x^2 + 10x + 2 \\[3ex] -6 = 3x^2 + 10x + 2 \\[3ex] 3x^2 + 10x + 2 = -6 \\[3ex] 3x^2 + 10x + 2 + 6 = 0 \\[3ex] 3x^2 + 10x + 8 = 0 \\[3ex] 3x^2 + 6x + 4x + 8 = 0 \\[3ex] 3x(x + 2) + 4(x + 2) = 0 \\[3ex] (x + 2)(3x + 4) = 0 \\[3ex] x + 2 = 0 \hspace{1em}OR\hspace{1em} 3x + 4 = 0 \\[3ex] x = -2 \hspace{1em}OR\hspace{1em} 3x = -4 \\[3ex] x = -2 \hspace{1em}OR\hspace{1em} x = -\dfrac{4}{3} \\[5ex] -2 \lt -\dfrac{4}{3} \\[5ex] $ ∴ the least value of x = −2
$ A.\;\; -1 \lt x \lt 12 \\[3ex] B.\;\; -1 \lt x \lt \dfrac{1}{12} \\[5ex] C.\;\; x \le -1 \;\;or\;\; x \ge \dfrac{1}{12} \\[5ex] D.\;\; x \le -1 \;\;or\;\; x \ge 12 \\[3ex] $
$ 11x + 12 \gt x^2 \\[3ex] x^2 \lt 11x + 12 \\[3ex] x^2 - 11x - 12 \lt 0 \\[3ex] (x + 1)(x - 12) \lt 0 \\[3ex] Assume:\;\;(x + 1)(x - 12) = 0 \\[3ex] x + 1 = 0 \;\;\;OR\;\;\; x - 12 = 0 \\[3ex] x = -1 \;\;\;OR\;\;\; x = 12 \\[3ex] Test\;\;Intervals\;\;are: \\[3ex] x \lt -1 \\[3ex] -1 \lt x \lt 12 \\[3ex] x \gt 12 \\[3ex] $
| Test Intervals: Let: |
x < −1 x = −2 |
−1 < x < 12 x = 0 |
x > 12 x = 13 |
| $x + 1$ | − | + | + |
| $x - 12$ | − | − | + |
| $(x + 1)(x - 12)$ | + | − | + |
The second test interval gives the solution of the inequality because a negative number is less than 0
Set Notation: {x | −1 < x < 12}
Interval Notation: (−1, 12)
Check
| LHS | RHS |
|---|---|
| $ 11x + 12 \\[3ex] 11(0) + 12 \\[3ex] 0 + 12 \\[3ex] 12 $ | $ x^2 \\[3ex] 0^2 \\[3ex] 0 $ |
| 12 > 0 | |
| Marks | 1 — 5 | 6 — 10 | 11 — 15 | 16 — 20 |
| Number of Students | 5 | 5 | x | 8 |
| Cumulative Frequency | 5 | 10 | 12 | y |
Find the value of $(2x + y)$
$ A.\;\; 38 \\[3ex] B.\;\; 34 \\[3ex] C.\;\; 28 \\[3ex] D.\;\; 24 \\[3ex] $
Based on the Cumulative Frequency:
$ 5 \\[3ex] 5 + 5 = 10 \\[3ex] 10 + x = 12 \implies x = 12 - 10 = 2 \\[3ex] 12 + 8 = y \implies y = 20 \\[5ex] 2x + y \\[3ex] = 2(2) + 20 \\[3ex] = 4 + 20 \\[3ex] = 24 $
$ A.\;\; \dfrac{3}{4}\sqrt{2} \\[5ex] B.\;\; \dfrac{4}{3}\sqrt{2} \\[5ex] C.\;\; -\dfrac{3}{4}\sqrt{2} \\[5ex] D.\;\; -\dfrac{4}{3}\sqrt{2} \\[5ex] $
$ \sin^2 y + \cos^2 y = 1 ...\text{Pythagorean Identity} \\[3ex] \sin^2 y = 1 - \cos^2 y \\[3ex] = 1 - \left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)^2 \\[5ex] = 1 - \dfrac{1}{9} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{8}{9} \\[5ex] \sin y = \pm \sqrt{\dfrac{8}{9}} \\[5ex] \text{But } 90^\circ \lt y \lt 180^\circ \;\;\text{is in the 2nd Quadrant} \\[3ex] \text{In the 2nd Quadrant, sine is positive} \\[3ex] \implies \\[3ex] \sin y = \sqrt{\dfrac{8}{9}} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{\sqrt{4 * 2}}{3} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{3} \\[5ex] \csc y = \dfrac{1}{\sin y} ...\text{Reciprocal Identity} \\[5ex] \csc y = 1 \div \sin y \\[3ex] = 1 \div \dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{3} \\[5ex] = 1 * \dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{2}} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{2}} * \dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{2 * 2} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{4} $
Calculate the maximum height reached.
[Take g = 10$ms^{-2}$]
$ A.\;\; 10.0 m \\[3ex] B.\;\; 9.6 m \\[3ex] C.\;\; 7.2 m \\[3ex] D.\;\; 6.4 m \\[3ex] $
We shall use one of the equations of motion:
$ v^2 = u^2 + 2as \\[3ex] $ When the ball is thrown vertically upwards:
(1.) The final velocity, v is zero.
But we have an initial velocity, u = 12$ms^{-1}$
(2.) The acceleration, a is negative because it is working against gravity
Hence, it is the negative value of the acceleration due to gravity
a = −g
(3.) We shall take the distance, s to be the maximum height, H
So, we have
$ v^2 = u^2 + 2as \\[3ex] becomes \\[3ex] v^2 = u^2 - 2gH \\[3ex] 0^2 = 12^2 - 2(10) * H \\[3ex] 0 = 144 - 20H \\[3ex] 20H = 144 \\[3ex] H = \dfrac{144}{20} \\[5ex] H = 7.2\;m $
$ A.\;\; x^2 + y^2 - 12x + 22y + 93 = 0 \\[3ex] B.\;\; x^2 + y^2 - 12x - 22y + 93 = 0 \\[3ex] C.\;\; x^2 + y^2 - 12x + 22y - 93 = 0 \\[3ex] D.\;\; x^2 + y^2 - 12x - 22y - 93 = 0 \\[3ex] $
The equation of a circle in the (x, y) coordinate plane with center (h, k) and radius, r is:
$ (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2 \\[3ex] Center:\;\; (h, k) = (6, -11) \\[3ex] h = 6 \\[3ex] k = -11 \\[3ex] r = 8 \\[3ex] \implies \\[3ex] (x - 6)^2 + (y - -11)^2 = 8^2 \\[3ex] (x - 6)^2 + (y + 11)^2 = 64 \\[3ex] [(x - 6)(x - 6)] + [(y + 11)(y + 11)] - 64 = 0 \\[3ex] (x^2 - 6x - 6x + 36) + (y^2 + 11y + 11y + 121) - 64 = 0 \\[3ex] x^2 - 12x + 36 + y^2 + 22y + 121 - 64 = 0 \\[3ex] x^2 + y^2 - 12x + 22y + 93 = 0 $
What is the probability that it will consist of a boy and a girl?
$ A.\;\; \dfrac{15}{28} \\[5ex] B.\;\; \dfrac{5}{28} \\[5ex] C.\;\; \dfrac{3}{28} \\[5ex] D.\;\; \dfrac{2}{7} \\[5ex] $
total number = 5 boys and 3 girls = 8 people
selected number = 1 boy and 1 girl = 2 people
Let:
S = sample space
$n(S) = C(8, 2)$
A = event of selecting 1 boy from 5 boys
$n(A) = C(5, 1)$
B = event of selecting 1 girl from 3 girls
$n(B) = C(3, 1)$
$ C(n, r) = \dfrac{n!}{(n - r) r!} \\[5ex] n(S) = C(8, 2) = \dfrac{8!}{(8 - 2)! * 2!} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{8 * 7 * 6!}{6! * 2 * 1} \\[5ex] = 4 * 7 \\[3ex] = 28 \\[5ex] n(A) = C(5, 1) = \dfrac{5!}{(5 - 1)! * 1!} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{5 * 4!}{4! * 1} \\[5ex] = 5 \\[5ex] n(B) = C(3, 1) = \dfrac{3!}{(3 - 1)! * 1!} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{3 * 2!}{2! * 1} \\[5ex] = 3 \\[5ex] $ Probability of selecting 1 boy from 5 boys AND 1 girl from 3 girls is:
$ = \dfrac{n(A) * n(B)}{n(S)} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{5 * 3}{28} \\[5ex] = \dfrac{15}{28} $

If they stick together after collision, find their common velocity.
$ A.\;\; 1.6ms^{-1} \\[3ex] B.\;\; 2.8ms^{-1} \\[3ex] C.\;\; 3.2ms^{-1} \\[3ex] D.\;\; 3.6ms^{-1} \\[3ex] $
Let the:
First body be P: mass of 6 kg and velocity of 2 m/s
Second body be Q: mass of 4 kg and velocity of 4 m/s
Momentum = mass × velocity
$ \underline{\text{Before Collision}} \\[3ex] \text{Momentum of Body P} = 6 \times 2 = 12\;kgm/s \\[3ex] \text{Momentum of Body Q} = 4 \times 4 = 16\;kgm/s \\[3ex] \text{Total Momentum} = 12 + 16 = 28\;kgm/s \\[5ex] \underline{\text{After Collision}} \\[3ex] \text{Mass of P and Q after they stick together} = 6 + 4 = 10\;kg \\[3ex] \text{Let the common velocity} = v\;m/s \\[3ex] \text{Total Momentum} = 10 \times v = 10v\;kgm/s \\[5ex] \text{Based on the Principle of Conservation of Momentum:} \\[3ex] 28 = 10v \\[3ex] 10v = 28 \\[3ex] v = \dfrac{28}{10} \\[5ex] v = 2.8\;kgms^{-1} $


